Ammonia-Powered Zero-Emission Trucks: Transforming the Transportation Landscape

The implications for the trucking industry are considerable. The advent of ammonia as a fuel source brings the day we can buy a truck powered by a hydrogen fuel cell closer and at a lower cost.
The innovative company Amogy Inc. has taken a significant stride towards a greener future by successfully testing the world’s first ammonia-powered, zero-emission semi-truck. Following successful trials with a 5kW drone and a 100kW John Deere farm tractor, Amogy scaled up its ammonia-to-power technology to a hefty 300 kW.
Emergence of Ammonia-Powered Zero-Emission Trucks: Revolutionizing Transportation with Ammonia Fuel

Amogy’s proprietary technology cracks ammonia on-board into hydrogen, which then fuels the vehicle.
Amogy’s proprietary technology cracks ammonia on-board into hydrogen, which then fuels the vehicle. The energy density of liquid ammonia is approximately three times greater than compressed hydrogen, and it requires significantly less energy, making it cost-effective to store and transport. The company’s technology is a breakthrough in emission reduction and offers a clear path to a zero-carbon fuel value chain across all heavy-duty transportation sectors.
“The implications for the trucking industry are considerable. The advent of ammonia as a fuel source brings the day we can buy a truck powered by a hydrogen fuel cell closer and at a lower cost.” – Jimmy Faria, a chemical engineer at the University of Twente in the Netherlands
Enjoying our insights?
Subscribe to our newsletter to keep up with the latest industry trends and developments.
Stay Informed
Global Ammonia Availability and Accessibility
As a global commodity, ammonia is already produced and transported in vast quantities – 200 million tons each year, making it an ideal and accessible alternative fuel. Ammonia’s global availability and existing infrastructure make it an optimal fuel to accelerate the decarbonization of heavy transportation, according to Seonghoon Woo, CEO at Amogy.
Hydrofuel Canada’s Novel Ammonia Application

Hydrofuel Canada proposes an alternate way to use ammonia – direct injection into an internal combustion engine, aided by a small amount of diesel or biodiesel for combustion.
Meanwhile, Hydrofuel Canada proposes an alternate way to use ammonia – direct injection into an internal combustion engine, aided by a small amount of diesel or biodiesel for combustion. This multi-fuel motor approach requires slight engine modifications, but the company assures it’s an easy retrofit.
Ammonia’s Historical Uses and Modern Revival
Historically, such uses of ammonia can be traced back to the 1800s, including an ammonia-fueled streetcar in New Orleans in 1871. During World War II, liquid ammonia was a common replacement for scarce diesel or gasoline in European vehicles. Today, numerous projects across the world are aimed at using ammonia as a carbon-free fuel for power generation, off-grid applications, and internal combustion engines.
The Synergy of Ammonia and Hydrogen Fuel Cells
Ammonia’s global availability and existing infrastructure make it an optimal fuel to accelerate the decarbonization of heavy transportation.
In the broader perspective, ammonia’s most crucial role will likely be as an energy carrier for hydrogen to power fuel cells, effectively paving the way to a hydrogen economy. Despite its unpleasant smell and caustic nature, ammonia possesses an energy density by volume nearly double that of hydrogen.
The Circular Journey of Green Ammonia Production
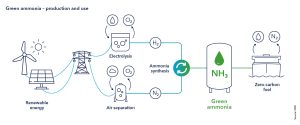
- The creation of green ammonia, an essential component in the production of green hydrogen, is not feasible using the conventional method – the Haber-Bosch process.
- This process involves stripping hydrogen from natural gas using steam, which unfortunately results in a significant carbon footprint,“`html
emitting two tons of CO2 for every ton of ammonia produced. - Therefore, the future of green ammonia production lies in utilizing renewable electricity to produce hydrogen via electrolysis, eliminating the need for natural gas and significantly reducing emissions.
Global Shift to Green Ammonia
Projects aimed at green ammonia production are already underway worldwide. For instance, a significant effort in Saudi Arabia is projected to produce a million tons of ammonia annually by 2025. In contrast, a smaller-scale initiative in Louisiana is expected to produce 20,000 tons annually this year. These developments indicate a global shift towards a more sustainable and cleaner fuel alternative.
Overcoming the Barriers of Hydrogen Adoption with Ammonia-Powered Zero-Emission Trucks
Ammonia’s easier storage, shipping, and distribution capabilities solve one of the largest obstacles to hydrogen adoption – the high costs of storage and transportation. Ammonia only needs to be cooled to about -37 degrees Fahrenheit to remain liquid, compared to hydrogen’s -423 degrees Fahrenheit. It holds nearly 50% more hydrogen by volume than liquid hydrogen and can be “cracked” to provide hydrogen using inexpensive catalysts.

Ammonia’s most crucial role will likely be as an energy carrier for hydrogen to power fuel cells, effectively paving the way to a hydrogen economy.
The Green Ammonia Revolution

While pure hydrogen has been hailed as the fuel of the future, ammonia appears to be a more effective pathway.
The creation of green ammonia for green hydrogen is not feasible using the conventional method, which involves stripping hydrogen from natural gas using steam (the Haber-Bosch process). This method is not eco-friendly, emitting two tons of CO2 for every ton of ammonia produced. Hence, natural gas must be eliminated from the process, and hydrogen should be produced instead by electrolysis using renewable energy.
Global Efforts in Green Ammonia Production
From Canada to Australia, projects are already underway to produce green ammonia. The largest is in Saudi Arabia, projected to produce a million tons of ammonia annually by 2025. A more modest plant in Louisiana is expected to produce 20,000 tons annually this year.
Ammonia: The Preferred Route to a Hydrogen Economy
While pure hydrogen has been hailed as the fuel of the future, ammonia appears to be a more effective pathway. “It ticks all the boxes,” remarks Jimmy Faria, a chemical engineer at the University of Twente in the Netherlands.
What Does This Mean for the Trucking Industry? The Impact of Ammonia-Powered Zero-Emission Trucks on the Trucking Industry
The implications for the trucking industry are considerable. The advent of ammonia as a fuel source brings the day we can buy a truck powered by a hydrogen fuel cell closer and at a lower cost. Unless battery technology evolves to provide the range needed, trucks powered by hydrogen fuel cells may soon be a desirable option.
In conclusion, the development and successful testing of ammonia-powered zero-emission trucks by companies like Amogy Inc. and Hydrofuel Canada signals a significant step towards a greener, more sustainable future. With the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry, ammonia as an alternative fuel is a game-changer.
Explore More News and Resources:
- Amogy presents world’s first ammonia-powered, zero-emission semi showcasing retrofitted 2018 Freightliner Cascadia.
- Learn about the strategic shift in the Nikola EV production pause sparks strategic shift toward hydrogen and autonomous technologies.
- Discover how Paccar and Toyota are revolutionizing the transport industry with their next-gen hydrogen fuel cell trucks.
- Uncover Cummins zero-emission solutions with Accelera breakthroughs in decarbonization for fleets.
- Keep up with Global Trends in the trucking industry.
Explore Industry Resources and Insights:
- Learn about the innovative solutions of Amogy Inc. in creating emission-free, energy-dense ammonia power.
- Historic demonstration featured Amogy’s ammonia-powered, zero-emissions energy system in use in a heavy-duty vehicle for the first time.
- Discover Hydrofuel Inc.’s leading role in the development of ammonia fuel and energy technologies.
- Understand the commercial demonstration project by Hydrofuel to convert diesel gensets and transport trucks to run on ammonia fuel.
- Explore the patented hydrogen ammonia fuel release and energy station tech gained by Hydrofuel.




















